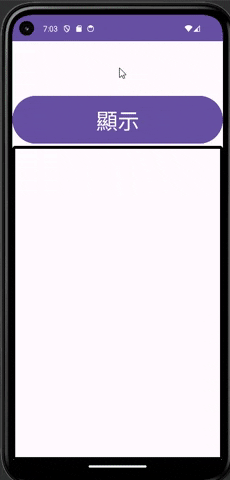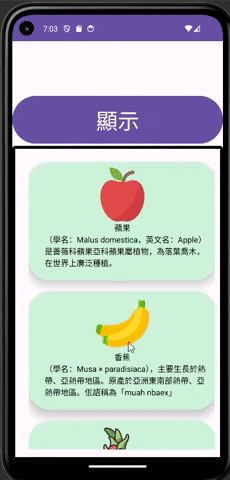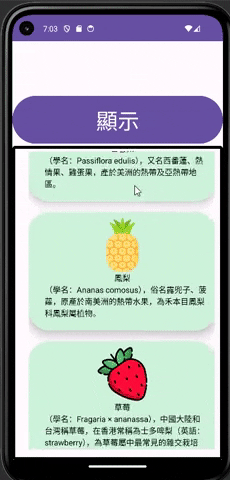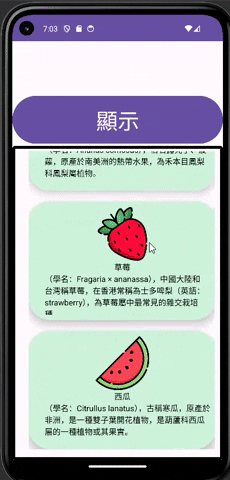
CardView就相當於一個卡片的介面,我可以在裡面加入各種物件,例如:TextView、Button、ImageView......,透過這種方式就可以製作各式各樣的卡片,通常CardView也不會只使用一個來表達訊息,但是太多個手機介面也放不下,所以通常就會放到像RecyclerView或ScrollView這種能夠滑動內容的物件裡面做顯示。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:gravity="center|top">
<Space
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="0.1" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="0.1"
android:textSize="40sp"
android:text="顯示" />
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:paddingTop="10sp"
android:background="@drawable/border"
android:id="@+id/recyclerView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="0.6"
android:paddingLeft="30sp"
android:paddingBottom="20dp"
tools:listitem="@layout/recycleritem_cardview"/>
</LinearLayout>
這次的的實作我添加了一個按鈕還有RecyclerView,當按下按鈕後就呼叫設定RecyclerView的方法。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.cardview.widget.CardView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="350dp"
android:layout_height="220dp"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
app:cardBackgroundColor="#CDF3DB"
app:cardCornerRadius="40dp"
app:cardElevation="10dp"
app:contentPadding="10sp"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_title"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="TextView"
android:gravity="center"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="15sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingLeft="20sp"
android:text="TextView"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="15sp"/>
</LinearLayout>
</androidx.cardview.widget.CardView>
CardView比較常會使用到的設定
app:cardBackgroundColor="#CDF3DB"
app:cardCornerRadius="40dp"
app:cardElevation="10dp"
app:contentPadding="10sp"
cardBackgroundColor,可以設定背景的顏色。cardCornerRadius,可以設定圓角。cardElevation,可以設定陰影。contentPadding,可以設定邊框跟內容的距離。<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item>
<shape>
<stroke android:color="@color/black"
android:width="5dp"/>
<corners android:radius="3dp"/>
<padding android:left="15sp"
android:right="15sp"/>
</shape>
</item>
</selector>
其實CardView結合RecyclerView不用想的太困難,就跟一般在使用RecyclerView的用法一樣,可以把CardView想成是RecyclerView的Item,所以在綁定頁面時也是一樣綁定到CardView,接著就可以對上面的物件進行控制了
private Button button;
private RecyclerView recyclerView;
private MyListAdapter myListAdapter;
private ArrayList<HashMap<String,String>> mArrayList;
private List<Integer> list;
這次宣告我除了原本會使用的ArrayList外,還宣告了一個List,這是因為圖片存在Drawable中會以id的方式紀錄,而這個id是整數型態,而一個ArrayList又只能儲存一種型態的資料,所以才要用到兩個陣列來儲存
button = findViewById(R.id.button);
recyclerView = findViewById(R.id.recyclerView);
makeData();
button.setOnClickListener(view -> setRecyclerView(mArrayList,list));
綁定物件id還有建造假資料跟按鈕的點擊事件
private void setRecyclerView(ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>> mArrayList ,List<Integer> list) {
myListAdapter = new MyListAdapter(mArrayList,list);
recyclerView.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager(this));
recyclerView.setAdapter(myListAdapter);
}
設定RecyclerView
private void makeData() {
mArrayList = new ArrayList<>();
list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
list.add(getResources().obtainTypedArray(R.array.images).getResourceId(i,0));
hashMap.put("title",getResources().obtainTypedArray(R.array.title).getString(i));
hashMap.put("content",getResources().obtainTypedArray(R.array.content).getString(i));
mArrayList.add(hashMap);
}
}
因為資料是存在strings裡面,這裡就直接獲取相關資源,用陣列將抓取下來的資料存起來,最後就會因為按下按鈕而將資料傳進RecyclerView
private ArrayList<HashMap<String,String>> mArrayList;
private List<Integer> mlist;
public MyListAdapter(ArrayList<HashMap<String,String>> arrayList, List<Integer> list){
this.mArrayList = arrayList;
this.mlist = list;
}
在建構元的部分指定要傳入的資料,其他綁定物件id跟介面的部分都跟之前一樣
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull MyListAdapter.ViewHolder holder, int position) {
holder.imageView.setImageResource(mlist.get(position));
holder.title.setText(mArrayList.get(position).get("title"));
holder.content.setText(mArrayList.get(position).get("content"));
}
imageView的部分要使用setImageResource並且指定存放的圖片資料id。
